Understanding Basic Surgical Instruments: A Comprehensive Guide
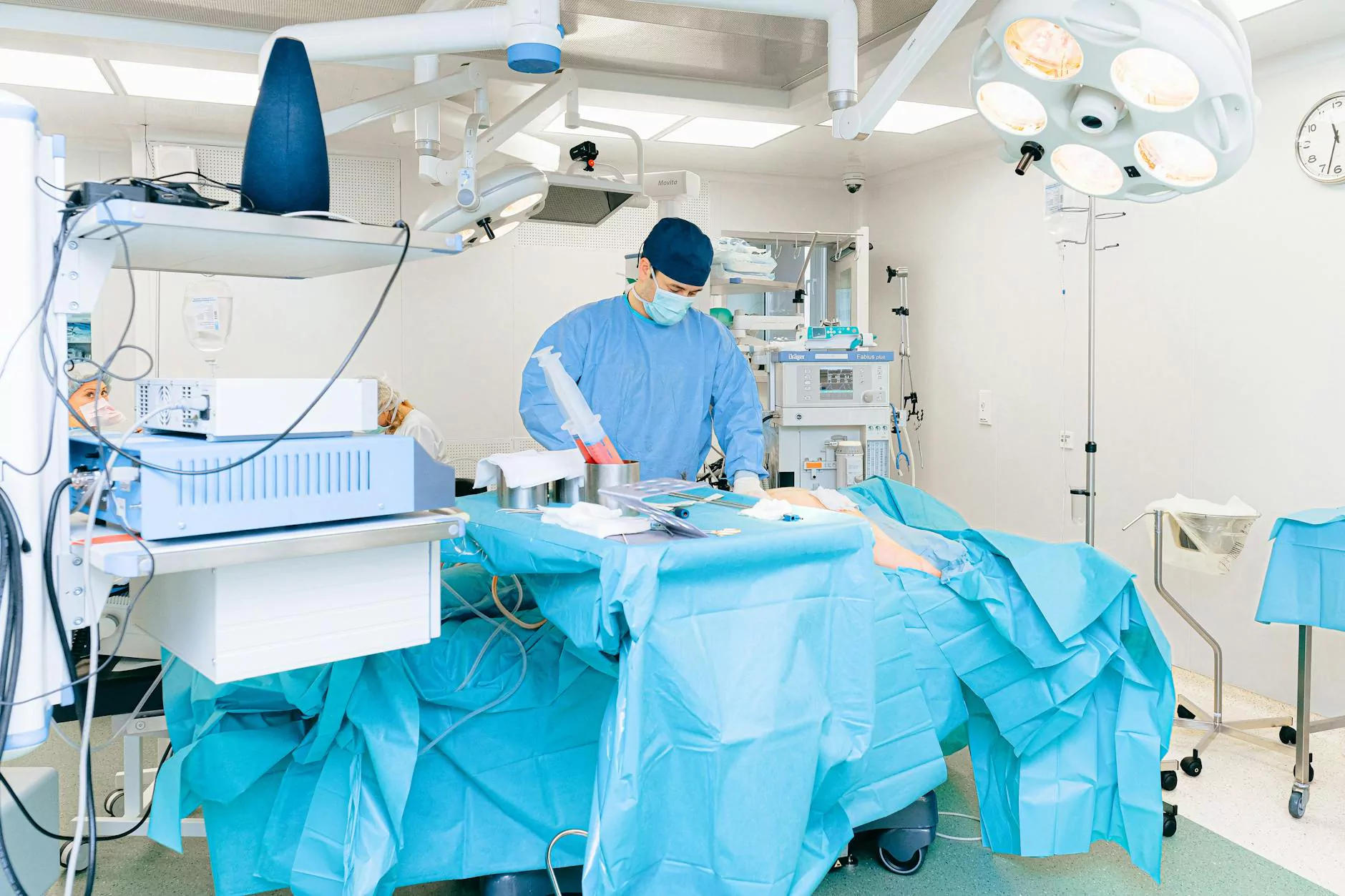
Surgical instruments are essential tools in the medical field, playing a crucial role in various procedures. Among them, basic surgical instruments form the backbone of surgical operations, ensuring that surgeries are performed safely and effectively. In this article, we will delve deep into the world of these instruments, covering their types, uses, and significance in health and medical fields.
1. What Are Basic Surgical Instruments?
Basic surgical instruments refer to the fundamental tools that surgeons and medical professionals utilize during surgical procedures. These instruments are designed for various tasks, such as cutting, dissecting, grasping, clamping, and suturing. Without these tools, many surgical operations would not be possible, highlighting their importance in modern medicine.
1.1 The Importance of Basic Surgical Instruments
The role of basic surgical instruments cannot be overstated. They are crucial for:
- Precision: They allow surgeons to perform delicate operations with accuracy.
- Efficiency: They enable quick and effective procedures, minimizing patient recovery time.
- Safety: Proper instruments reduce the risk of complications during surgery.
- Versatility: Many instruments can be adapted for various types of surgeries, making them invaluable in the operating room.
2. Types of Basic Surgical Instruments
Basic surgical instruments can be categorized into several types based on their functions. Below are the primary categories of these instruments:
2.1 Cutting Instruments
Cutting instruments are designed to cut tissues and organs. The most common types include:
- Scalpels: Used for making incisions.
- Scissors: Different types are used for various applications, such as micro-dissection or cutting sutures.
- Knives: Specialized knives for particular surgical tasks.
2.2 Grasping Instruments
Grasping instruments help surgeons hold and manipulate tissues. Key types consist of:
- Forceps: Used to grasp tissues; they come in various designs.
- Tissue Forceps: Equipped with teeth or serrations to grip delicate tissues.
- Hemostatic Forceps: Clamps that control bleeding by occluding blood vessels.
2.3 Clamping Instruments
Clamping instruments are critical in controlling bleeding and holding tissues. Common examples include:
- Hemostats: Used to clamp blood vessels during surgery.
- Clamps: Applied to hold tissues in place and allow surgical manipulation.
2.4 Suturing Instruments
Suturing instruments are utilized in closing incisions or wounds. These include:
- Suture Needles: Designed to carry suture material through tissues.
- Suture Scissors: Specialized for cutting sutures after a procedure.
- Needle Holders: Used to securely grip and guide needles during suturing.
3. Material and Construction of Surgical Instruments
Understanding the materials and construction of basic surgical instruments is essential for quality and durability. Most instruments are made from:
- Stainless Steel: Known for its corrosion resistance and strength, making it the most common material.
- Plastic: Used for disposable instruments in certain cases to enhance safety.
- Titanium: Lightweight and exceptionally strong, often used for specialized instruments.
4. The Sterilization Process
The sterilization of basic surgical instruments is vital to prevent infections during surgeries. This process involves several steps:
- Cleaning: Instruments must be thoroughly cleaned to remove all organic material.
- Disinfection: Application of chemical agents to kill pathogens.
- Sterilization: Common methods include steam sterilization, ethylene oxide gas, and hydrogen peroxide plasma.
5. The Role of Basic Surgical Instruments in Various Health Markets
Different health markets rely heavily on basic surgical instruments. They are integral across various specialties:
5.1 In Hospital Settings
Hospitals require a significant inventory of surgical instruments in operating rooms, emergency departments, and outpatient surgical centers. They are essential in:
- General Surgery: Basic instruments are used in almost every surgical procedure.
- Orthopedics: Specialized instruments assist in bone surgeries and reconstructive procedures.
- Ophthalmology: Fine instruments designed for eye surgeries.
5.2 In Ambulatory Surgical Centers
Ambulatory surgical centers often focus on outpatient procedures, necessitating high-quality basic surgical instruments that can be sterilized and reused. Their importance includes:
- Efficiency: Quick turnovers of surgeries demand reliable instruments.
- Cost-effectiveness: Investing in durable instruments reduces long-term costs.
5.3 In Research and Development
Basic surgical instruments are also critical in medical research. Researchers rely on these tools for:
- Experimental Surgeries: Clinical trials require precise instruments to test new techniques.
- Training: Medical students and residents practice using basic instruments.
6. Innovations and the Future of Surgical Instruments
The field of surgical instruments is continuously evolving, with innovations aimed at improving performance and outcomes. Future trends include:
- Smart Instruments: Incorporating technology to assist surgeons with analytics and data.
- Robotic Surgery Tools: Development of advanced instruments that enhance precision and minimize invasiveness.
- Biodegradable Instruments: Focusing on sustainability through the use of eco-friendly materials.
7. Conclusion
In summary, basic surgical instruments are foundational elements in every surgical procedure, regardless of complexity. Their reliability, functionality, and safety are critical to successful outcomes in the medical field. As technology advances, we can expect even more innovations that will enhance the performance of these essential tools, ultimately improving patient care and surgical success rates.
For healthcare providers and medical professionals, choosing the right instruments from a trusted supplier like new-medinstruments.com ensures that they are equipped to deliver the highest standards of care to their patients. The right surgical instruments make all the difference in surgical precision and patient outcomes.









